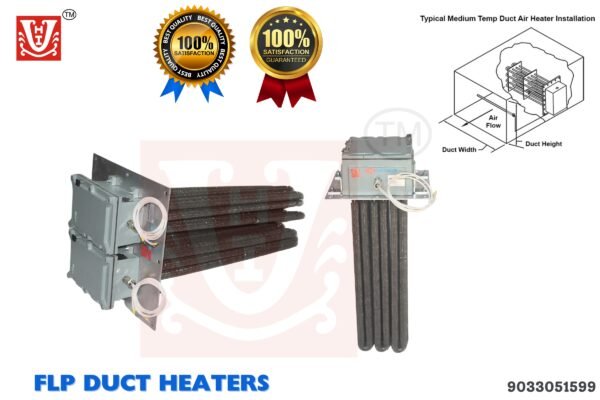
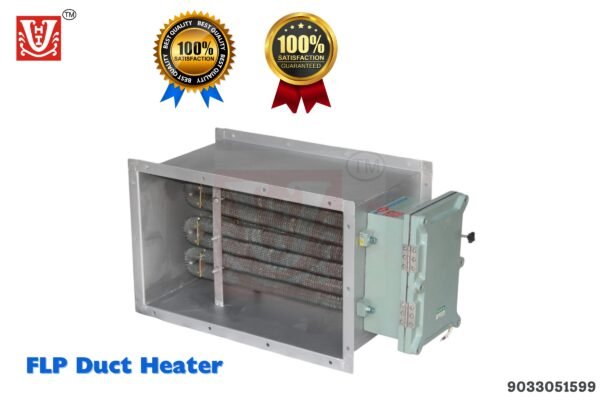
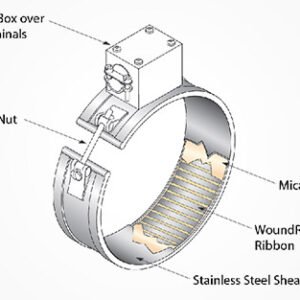
Duct Heater
A Duct Heater is an electric or gas-powered heating unit installed in air ducts to provide controlled heating for HVAC systems. It is commonly used in industrial, commercial, and residential applications to maintain desired air temperatures. Duct heaters consist of heating elements, controls, and safety features such as thermal cutoffs. They are available in various sizes, power ratings, and configurations to suit different airflow and heating requirements.
- Description
Description
Description:
A Duct Heater is an electric heating device designed to be installed within air ducts for efficient heating in HVAC systems. It provides uniform heating for air circulation in industrial, commercial, and residential applications.
Key Features:
-
Heating Elements: High-quality stainless steel or nickel-chromium alloy for durability.
-
Customizable Design: Available in various sizes, wattages, and voltage configurations.
-
Control Options: Thermostat, temperature sensors, and electronic controllers for precise heating.
-
Safety Mechanisms: Thermal cutoffs, airflow sensors, and high-temperature protection.
-
Application: Suitable for air handling units, process heating, and space heating.
Technical Specifications:
-
Power Rating: Ranges from 1 kW to 500 kW (customizable).
-
Voltage Options: 230V, 415V, or as per requirement.
-
Material: Stainless steel or galvanized steel casing.
-
Mounting Type: Flanged or slip-in installation.
Applications:
-
HVAC systems for buildings and industrial plants.
-
Drying and curing processes in manufacturing.
-
Air heating in clean rooms and laboratories.
1. General Specifications:
-
Type: Electric Duct Heater
-
Construction: Stainless Steel / Galvanized Steel / Mild Steel
-
Installation: Flanged or Slip-in Mounting
-
Heating Elements: Nickel-Chromium (NiCr) / Stainless Steel / Finned Tubular Elements
2. Electrical Ratings:
-
Voltage Options: 230V / 415V / 480V / 600V (Customizable)
-
Power Range: 1 kW – 500 kW
-
Phase: Single-phase / Three-phase
-
Control System: ON/OFF, SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier), or Contactor Control
3. Temperature Control & Safety:
-
Temperature Range: Up to 600°C
-
Thermal Protection: Automatic Reset & Manual Reset Thermal Cutoff
-
Airflow Switch: Prevents operation without sufficient airflow
-
Insulation Resistance: High Dielectric Strength to Prevent Leakage
4. Mechanical & Material Features:
-
Casing Material: Stainless Steel / Galvanized Steel / Aluminum
-
Element Type: Open Coil / Finned Tubular / Tubular Elements
-
Air Velocity Requirement: Minimum 2 m/s for efficient heating
5. Applications:
-
HVAC Systems & Air Handling Units
-
Industrial Drying & Process Heating
-
Clean Rooms, Laboratories, and Pharmaceutical Industry
-
Food Processing & Packaging Industry
-
Installation Guidelines:
1. Pre-Installation Checks:
-
Ensure the power supply matches the heater’s voltage and phase requirements.
-
Check that the duct size and airflow meet the heater’s specifications.
-
Ensure proper clearance around the heater for safety and maintenance.
-
Inspect the heater for any physical damage before installation.
2. Mounting & Positioning:
-
Install the heater horizontally or vertically, depending on the model specifications.
-
Use flange or slip-in mounting for secure installation.
-
Position the heater downstream of fans and filters for even heat distribution.
-
Ensure minimum airflow (typically 2 m/s) to prevent overheating.
3. Electrical Connections:
-
Use heat-resistant wiring as per the electrical load.
-
Connect the heater to a dedicated circuit breaker for safety.
-
Install temperature sensors, airflow switches, and safety relays as per the control system.
-
Verify grounding to prevent electrical hazards.
Maintenance & Safety
1. Routine Maintenance:
-
Inspect Heating Elements: Check for signs of wear, corrosion, or overheating.
-
Clean the Heater: Remove dust and debris to ensure efficient heat transfer.
-
Check Electrical Connections: Tighten loose terminals and inspect for insulation damage.
-
Test Safety Devices: Verify the operation of thermal cutoffs, airflow switches, and relays.
2. Troubleshooting Tips:
Issue Possible Cause Solution Heater not turning on No power supply Check wiring and circuit breakers Overheating or tripping Low airflow / blocked ducts Ensure proper airflow and clean ducts Uneven heating Faulty elements Inspect and replace damaged heating elements Electrical sparking Loose connections Tighten all terminals and check for short circuits 3. Safety Precautions:
✅ Always turn off power before maintenance.
✅ Ensure proper grounding to prevent electrical hazards.
✅ Do not operate the heater without airflow.
✅ Use only manufacturer-recommended replacement parts. -